Article Series: Transforming Public Sector Data: A Strategic Guide to Modernization
This is the first article in a series on data modernization in the public sector. In this article, we provide an overview of data modernization and explore a proven framework for successful implementation. In future articles in this series, we will dive deeper into the key data modernization elements and best practices critical to ensuring public sector organizations are poised to respond to the ever-evolving challenges of the modern, data-driven world.
Written by: Matthew Fisher, Esq., LL.M., MBA, Senior Management Consultant
Data plays an increasingly vital role in the modern world. The volume of data continues to grow at an unprecedented rate due to the influx of new sources and types of data. As a result, many public sector organizations seek to adapt their legacy systems to meet these evolving needs, which can be costly, complex, and challenging to maintain. These outdated systems often contain siloed data and are reliant on manual processes, which can negatively impact the quality and utility of the data.
In order to fully leverage data’s potential, public sector organizations must update and adapt their data infrastructure, technologies, and practices to meet the rapidly changing business needs and digital landscape. This transformative process is called Data Modernization, and it is critical for public sector organizations aiming to enhance service delivery, improve decision-making, and effectively respond to the evolving needs of the residents and communities they serve.
What is Data Modernization?
Data modernization is the process of transforming the way an organization collects, stores, manages, and utilizes data across the data lifecycle. Benefits of data modernization include:
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Accessible, centralized data drives enhanced decision-making.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined data processes increase workflow efficiencies.
- Improved Service Delivery: A holistic view of data helps tailor services to specific needs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Modern infrastructure can adapt to meet changing needs, technology, and laws and regulations.
While the benefits of data modernization are clear, the path to achieving these outcomes requires careful planning and execution.
A Framework for Data Modernization
Data modernization requires structure approach to help ensure modernization efforts are aligned with organizational goals through a shared vision, needs and gaps are addressed, and are sustainable in the long-term. To successfully implement a data modernization initiative, public sector leaders should follow the below structured approach.
- Align:
Start the data modernization journey by creating a foundational shared vision for the future, aligning business and data strategies. A shared vision establishes a clear picture of what the organization aims to achieve through data modernization. A business strategy is a high-level plan created by an organization to achieve its overarching goals and objectives. A data strategy, on the other hand, is a detailed plan that outlines how an organization will manage, analyze, and use its data to support its business goals. It focuses on making data a strategic asset that can drive decision-making and improve overall business performance.
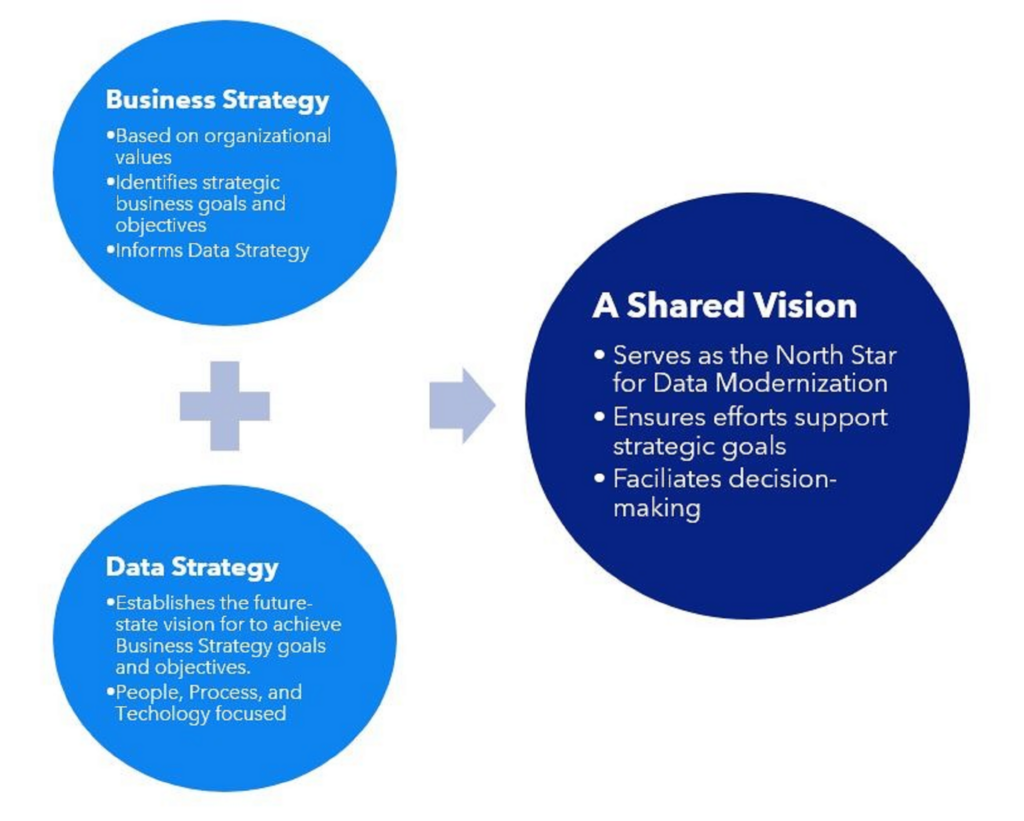
Engage stakeholders to ensure their needs and perspectives are considered and built into this shared vision, fostering critical buy-in support for data modernization efforts. By creating a shared vision at the beginning of a data modernization project, business and data strategies are aligned to maximize project impact, ensure the efficient use of resources, and lay the foundation for a data-driven future.
Engage stakeholders to ensure their needs and perspectives are considered and built into this shared vision, fostering critical buy-in support for data modernization efforts. By creating a shared vision at the beginning of a data modernization project, business and data strategies are aligned to maximize project impact, ensure the efficient use of resources, and lay the foundation for a data-driven future.
- Assess
With a shared vision in place, the next critical step is to thoroughly understand the organization’s current state. Assess the organization’s current state of people, process and technology and identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. This provides context to the organization’s current level of maturity and benchmarks its performance against industry best practices and standards.
Various tools and frameworks can be utilized to gain a comprehensive understanding of the current state of its data capabilities and areas for improvement, including:
- Data Maturity Model: Evaluate how well an organization is managing and using data and how capable they are of implementing continuous improvement against defined standards. The maturity model helps identify opportunities for improvement based on the severity and impact of identified gaps. This enables measurement of progress for future modernization plans and initiatives by establishing a baseline.
- Gap Analysis: Compare the organization’s current data capabilities with the desired future state. The resulting analysis highlights specific gaps that need to be addressed to achieve modernization goals, setting the stage for development of the action plans.
- Benchmarking: Contrast organizational data management practices against industry standards. This helps identify best practices, as well as identify and prioritize gap areas where the organization lags by industry standards, providing insights into what needs to be improved to remain competitive.
- Workforce and Cultural Assessments: Evaluate the current skills, competencies, roles and responsibilities, and knowledge levels within the organization, particularly related to data and technology, helping ensure the organization possesses the required skills and is culturally ready to adapt to modern data management practices and technology. In addition to identifying skill and position gaps and training needs, surveys and interviews can provide additional qualitative into an organization’s culture and change readiness.
- Plan
Develop Action Plans that are forward-looking, flexible, scalable, and sustainable based on the gap analysis and prioritized based on impact, risk, and feasibility. These plans help make the shared vision for data modernization a shared reality, by detailing the people, process, and technology initiatives needed to achieve it, such as:
- People
- Enhance workforce skills in data and technology through professional development programs and culture initiatives.
- Use Organizational Change Management (OCM) to facilitate the adoption of new technologies, processes, and workflows.
- Redesign roles and responsibilities to implement data modernization and ensure robust data security, quality, and analytics.
- Process
- Develop a governance framework to develop and maintain data governance policies.
- Automate data management processes to gain efficiency, reduce risk of error, and improve data quality.
- Establish a process for identifying and evaluating data modernization initiatives.
- Technology
- Modernize data architecture to enhance scalability, flexibility, and performance.
- Leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to gain more value from data and drive decision-making.
- Ensure accessibility and security of data through integration into a centralized repository, such as an Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW) or Data Lake.
ISF and Data Modernization
ISF utilizes a holistic, adaptable, and iterative approach to help our clients not just keep pace with but excel in the rapidly shifting data ecosystem. Our recommendations are tailored to the client’s unique needs, leveraging our experience and expertise with emerging best practices and technologies to get the value from data they want and need but are not currently able to access and leverage.
ISF offers a number of services to help agencies meet their data modernization goals.
